Shutdown and Start sequence steps of Oracle RAC components
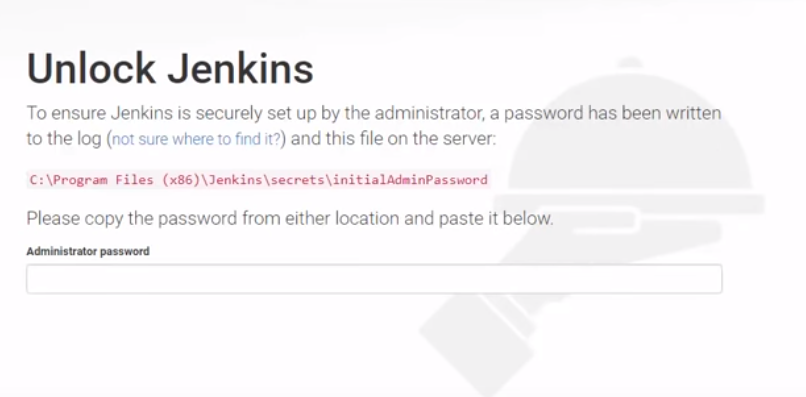
How to stop Oracle RAC (11g, 12c)?
You must perform these steps in the order listed to stop Oracle RAC:
- emctl stop dbconsole (11c only. In 12c DB Express replaces dbconsole and doesn’t have to be stopped )
- srvctl stop listener [-listener listener_name] [-node node_name] [-force] (stops all listener services)
- srvctl stop database -db db_unique_name [-stopoption stop_options] [-eval(12c only)] [-force] [-verbose]
- srvctl stop asm [-proxy] [-node node_name] [-stopoption stop_options] [-force]
- srvctl stop nodeapps [-node node_name] [-gsdonly] [-adminhelper] [-force] [-relocate] [-verbose]
- crsctl stop crs
How to Start Oracle RAC (11g, 12c)?
You must perform these steps in the order listed to start Oracle RAC:
1. crsctl start crs
2. crsctl start res ora.crsd -init
3. srvctl start nodeapps [-node node_name] [-gsdonly] [-adminhelper] [-verbose]
4. srvctl start asm [-proxy] [-node node_name [-startoption start_options]]
5. srvctl start database -db db_unique_name [-eval(12c only)]] [-startoption start_options] [-node node_name]
6. srvctl start listener [-node node_name] [-listener listener_name] (start all listener services)
7. emctl start dbconsole (11c only)
To start resources of your HA environment if that are still down(e.g. ora.ons, Listener):
crsctl start resource -all
DEBUG
Starting with Oracle 12c, the log and trace files of the clusterware files are stored in the Automatic Diagnostic Repository (ADR) under the ADR_HOME location $ADR_BASE/diag/crs/`hostname`/crs.
$ adrci
adrci> show homes
Cluster resources: CRS, HAS and cluster
How to display the status of resources in RAC?
Clusterware Resource Status Check : crsctl status resource -t (or shorter: crsctl stat res -t)
crsctl status resource -t (or shorter: crsctl stat res -t)
Find offline resources: crs_stat -t | grep -i offline
How to check the current status of a cluster?
crsctl check cluster
CRS-4537: Cluster Ready Services is online
CRS-4529: Cluster Synchronization Services is online
CRS-4533: Event Manager is online
To know the cluster name: olsnodes -c
How to check the current status of CRS?
crsctl check crs
CRS-4638: Oracle High Availability Services is online (has)
CRS-4537: Cluster Ready Services is online (crs)
CRS-4529: Cluster Synchronization Services is online (css)
CRS-4533: Event Manager is online
How to Stop/Start the local node?
crsctl stop has
This command will also abort the database and CRS. Local Listeners will stop and VIP listeners will migrate elsewhere.
crsctl start has
This command will start all the CRS components, listeners and the database.
How to Stop/Start the whole cluster?
crsctl stop cluster -all
crsctl start cluster -all
How to To start and stop oracle clusterware (CRS)?
crsctl stop crs
crsctl start crs
Manage Network components
How to display global public and global cluster_interconnect?
C:\Windows\system32>oifcfg ge34f
Heartbeat 194.56.67.0 global cluster_interconnect,asm
Production 10.356.3.0 global public
How to check if nodeapps running on a node?
srvctl status nodeapps [-n my-node]
For each VIP address: network enabled/disabled, running on node host1 or not running.
Nodeapps are standard set of oracle application services which are started automatically for RAC.
Node apps Include:
1) VIP
2) Oracle Net listeners
3) Global Service Daemon
4) Oracle Notification Service (ONS).
Nodeapp Services run on each node of the cluster. They switch over to other nodes through VIP during a failover.
How to check the SCAN Configuration?
The SCAN makes it possible to add or remove nodes from the cluster without needing to reconfigure clients.
Using CLUVFY to Confirm DNS is Correctly Associating the SCAN addresses.
cluvfy comp scan
Verifying Single Client Access Name (SCAN) …PASSED
Verification of SCAN was successful.
CVU operation performed: SCAN
Date: Oct 19, 2017 1:17:59 PM
CVU home: C:\…\grid_home\bin\..\
User: .\VFENOLL
Display the current configuration of the SCAN VIPs?
srvctl config scan
SCAN name: MY-CLUSTER-SCAN, Network: 1
Subnet IPv4: 10.104.2.0/255.255.255.0/Production, static
Subnet IPv6:
SCAN 1 IPv4 VIP: 10.404.2.677
SCAN VIP is enabled.
SCAN VIP is individually enabled on nodes:
SCAN VIP is individually disabled on nodes:
SCAN 2 IPv4 VIP: 10.404.2.618
SCAN VIP is enabled.
SCAN VIP is individually enabled on nodes:
SCAN VIP is individually disabled on nodes:
SCAN 3 IPv4 VIP: 10.404.2.619
SCAN VIP is enabled.
SCAN VIP is individually enabled on nodes:
SCAN VIP is individually disabled on nodes:
Display the status of SCAN VIPs and SCAN listeners?
srvctl status scan
SCAN VIP scan1 is enabled
SCAN VIP scan1 is running on node my-node1
SCAN VIP scan2 is enabled
SCAN VIP scan2 is running on node my-node2
SCAN VIP scan3 is enabled
SCAN VIP scan3 is running on node my-node1
If you want to add or modify a scan VIP: srvctl add | modify scan -n my-scan
To delete it: srvctl remove scan
Display the status of SCAN listeners?
srvctl status scan_listener
SCAN Listener LISTENER_SCAN1 is enabled
SCAN listener LISTENER_SCAN1 is running on node my-node1
SCAN Listener LISTENER_SCAN2 is enabled
SCAN listener LISTENER_SCAN2 is running on node my-node2
SCAN Listener LISTENER_SCAN3 is enabled
SCAN listener LISTENER_SCAN3 is running on node my-node1
If you want to add or remove a scan_listener: srvctl add | remove scan_listener
To change the port: srvctl modify scan_listener -p
Manage the Oracle Cluster Registry (OCR)
Verify the integrity of OCR?
cluvfy comp ocr -n all -verbose
Verifying OCR Integrity …PASSED
Verification of OCR integrity was successful.
CVU operation performed: OCR integrity
Date: Oct 11, 2017 4:56:01 PM
CVU home: C:\…grid_home\bin\..\
User: \VFENOLL
How to backup the OCR?
Oracle takes physical backup of OCR automatically every 3 hours. Default location is CRS_home/cdata/my_cluster_name/OCRBackup.
The ocrconfig tool is used to make daily copies of the automatically generated backup files.
Show backups:
ocrconfig -showbackup
Change default location of physical OCR copies:
ocrconfig -backuploc
After that, you have to copy these files on tape or in another backup location (cp -p -R CRS_home/cdata/my_cluster_name /u03/backups )
To do a manual backup:
ocrconfig -export /u03/backups/exports/OCR_exportBackup.dmp
How to recover OCR from physical or export backup?
Pre-requisite: All RAC components shutdow
Recover OCR from automatic physical backups:
crconfig -restore CRS_home/cdata/my_cluster_name/OCRBackup/backup00.ocr
Recover OCR from export backup:
ocrconfig -import /u03/backups/exports/OCR_exportBackup.dmp
How to backup the Voting disks?
In older versions of Oracle Clusterware you have to backup voting disks with the dd command.
Starting with Oracle Clusterware 11g Release 2 you no longer need to backup them. Voting disks are automatically backed up as a part of the OCR.
Manage database components
How to find the name of the database?
This name is useful as it is used in RAC commands with -d parameter.
With SQL*Plus:
connect / as sysdba
show parameter db_unique_name
With crsctl:
crsctl status resource -t | grep db
How to inspect the database configuration?
srvctl config database -d my-db-name
Database unique name: my-db-name
Database name: my-db-name
Oracle home: D:\oracle\db\product\12.2.0\dbhome_1
Oracle user: nt authority\system
Spfile: +DATA/my-db-name/PARAMETERFILE/spfile.272.9460543263
Password file: +DATA/my-db-name/PASSWORD/pwdmy-db-name.256.998734039
Domain:
Start options: open
Stop options: immediate
Database role: PRIMARY
Management policy: AUTOMATIC
Server pools:
Disk Groups: DATA,FRA
Mount point paths:
Services: my-db-name1,my-db-name2,srv1,srv2, srv3
Type: RAC
Start concurrency:
Stop concurrency:
Database instances: my-db-name1,my-db-name2
Configured nodes: node1,node2
CSS critical: no
CPU count: 0
Memory target: 0
Maximum memory: 0
Default network number for database services:
Database is administrator managed
Display name and the status of the instances in the RAC?
srvctl status database -d my-db-name
Instance my-db-name1 is running on node node1
Instance my-db-name2 is not running on node node2
To list just active nodes: olsnodes -s –t
How to start|stop the database?
srvctl stop database -d my-db-name -o immediate
srvctl start database -d my-db-name
How to start|stop one instance of the RAC?
srvctl start instance -d my-db-name -i my-db-name1
srvctl stop instance -d my-db-name -i my-db-name1
Use -force if the instance to stop is not on the local server
How to start and stop a PDB in Oracle RAC?
Stop a PDB
On the current node [or on all the nodes]:
ALTER PLUGGABLE DATABASE my-PDB-name CLOSE IMMEDIATE [Instances=all];
This will stop the associated service too.
Manually stopping the associated service will not close the PDB. You have to use this SQL command.
Start a PDB
On the current node [or on all the nodes]:
ALTER PLUGGABLE DATABASE my-PDB-name OPEN [Instances=all;]
You can also start the PDB with the associated service
This will NOT start the service(s) associated with this PDB.
How to stop and start a Listener?
srvctl stop listener -l LISTENER_NAME
srvctl start listener -l LISTENER_NAME